How to turn off DEP (Data Execution Prevention) in Windows
Data Execution Prevention, otherwise known as DEP, is a set of technologies incorporated into Windows XP SP2 and later that prevents code from being run in certain regions of memory that are for storage.
This helps to prevent all kinds of attacks and exploits that would normally be able to run freely on your system. Data Execution Prevention comes in two flavors, hardware-enforced DEP and software-enforced DEP.
Most users will never need to worry about DEP because it works in the background and normally only protects Windows system binaries or programs that “opt-in”. However, if DEP is turned on for all programs, it can cause issues with some certain programs.
DEP will sometimes shut down a program or process without any notification if it violates DEP. Normally, these are third-party or older programs not written properly for Windows.
You can turn off Data Execution Prevention for a particular program in Windows by following the steps below. Note that you can turn off DEP globally for the entire system, but it’s not recommended as it makes your computer less secure.
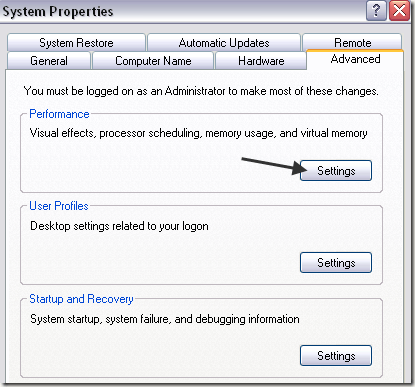
Step 1: Right-click on My Computer and choose Properties. Then click on the Advanced tab and then Settings under Performance.
Step 2: Now click on the Data Execution Prevention tab and you’ll see two radio buttons:

Step 3: Go ahead and click on Turn on DEP for all programs and services except those I select.
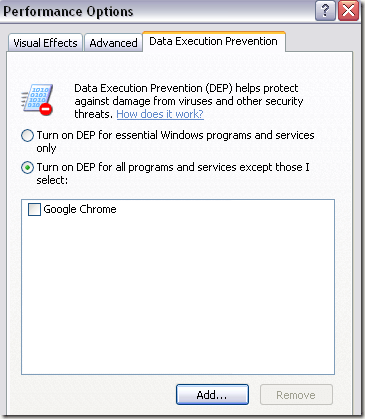
Step 4: Click the Add button and browse to the location of the executable for the program you want to remove from DEP protection.
After you do this, you should reboot your machine once in order for the changes to take place.
This helps to prevent all kinds of attacks and exploits that would normally be able to run freely on your system. Data Execution Prevention comes in two flavors, hardware-enforced DEP and software-enforced DEP.
Most users will never need to worry about DEP because it works in the background and normally only protects Windows system binaries or programs that “opt-in”. However, if DEP is turned on for all programs, it can cause issues with some certain programs.
DEP will sometimes shut down a program or process without any notification if it violates DEP. Normally, these are third-party or older programs not written properly for Windows.
You can turn off Data Execution Prevention for a particular program in Windows by following the steps below. Note that you can turn off DEP globally for the entire system, but it’s not recommended as it makes your computer less secure.
Step 1: Right-click on My Computer and choose Properties. Then click on the Advanced tab and then Settings under Performance.

Step 2: Now click on the Data Execution Prevention tab and you’ll see two radio buttons:

Step 3: Go ahead and click on Turn on DEP for all programs and services except those I select.

Step 4: Click the Add button and browse to the location of the executable for the program you want to remove from DEP protection.
After you do this, you should reboot your machine once in order for the changes to take place.








